In their tranquil Santa Fe estate, a Hollywood icon and his wife appeared to be enjoying a peaceful life. But when both were discovered dead in their home, investigators were stunned to find a disturbing twist — each had died from a completely different cause.
When Gene Hackman and his wife, Betsy Arakawa, were discovered dead under mysterious circumstances, the news sent shockwaves through the nation—prompting an extensive investigation and an outpouring of tributes for the legendary actor who embodied American toughness on screen.
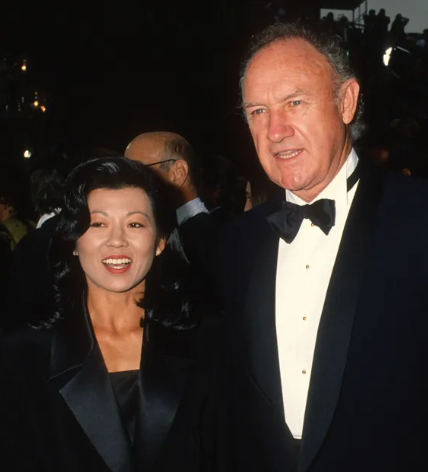

Betsy Arakawa and Gene Hackman attend the 65th Annual Academy Awards on March 29, 1993, in Los Angeles, California. | Source: Getty Images
Their deaths would unveil a chilling chain of events — a tale marked by perplexing medical twists, unanswered family questions, and layers of mystery that stunned even those closest to them. As investigators dug deeper, the complex and emotional story of the couple’s final days slowly came into focus.
How Did Gene Hackman and His Wife, Betsy Arakawa, Die?
On February 26, 2025, Gene Hackman, 95, and his wife, Betsy Arakawa, 65, were found dead inside their custom-renovated home just outside Santa Fe, New Mexico. The tragic discovery came after a pest-control worker, concerned by the couple’s uncharacteristic silence, alerted neighborhood security. Through a window, security personnel spotted the bodies and immediately contacted 9-1-1.
When first responders arrived, they found Hackman collapsed near the kitchen—his signature sunglasses and cane lying where they had fallen. Arakawa was discovered in a bathroom, unresponsive, with a collection of prescription medications nearby, mostly related to blood pressure and thyroid management.
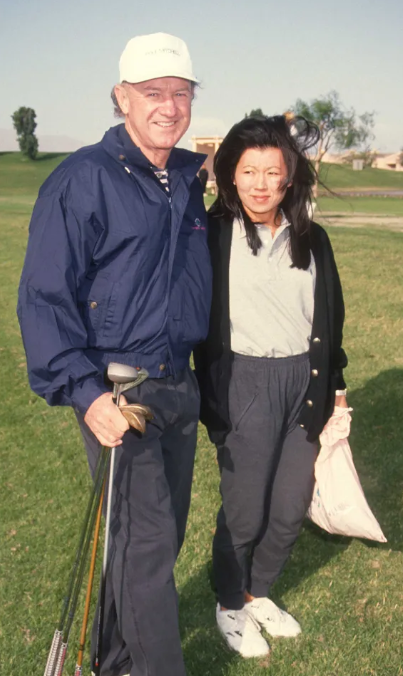

Gene Hackman and Betsy Arakawa at the Mission Hills Celebrity Sports Invitational on November 30, 1991, in California. | Source: Getty Images
One of their dogs was found dead in a kennel crate inside a closet near Betsy. Two other dogs, however, had survived the ordeal — one found inside the house, the other outside. The front door was unlocked, and the back door was left ajar, allowing the surviving animals to come and go freely. This discovery raised further questions about what had happened in the hours leading up to the deaths of Hackman and Arakawa, as it suggested an unsettling level of chaos within the otherwise serene home.
Detectives found no signs of forced entry, trauma, or any environmental hazards such as gas or carbon monoxide that could explain the deaths. However, pacemaker data revealed that Hackman had been deceased since February 17, a staggering nine days before their bodies were discovered. The advanced decomposition observed on both bodies confirmed this timeline, deepening the mystery surrounding their deaths and raising even more questions about what had transpired in those final days.
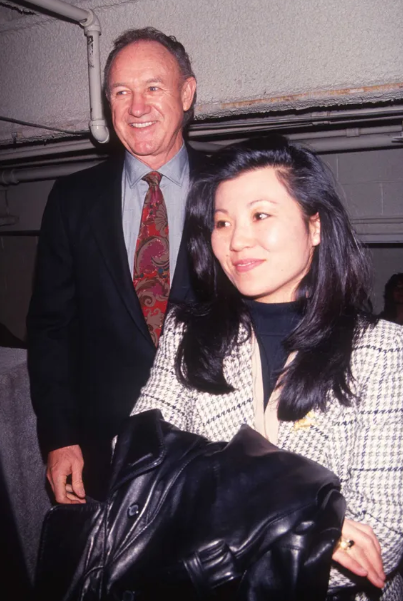

Gene Hackman and Betsy Arakawa at the D.W. Griffith Awards at the Equitable Center on February 24, 1992, in New York. | Source: Getty Images
The tragic loss of Gene Hackman and Betsy Arakawa prompted an emotional outpouring from the entertainment world. At the 2025 Academy Awards, Morgan Freeman paid tribute to Hackman, praising him as “a generous performer” and “a man whose gifts elevated everyone’s work.”
Viola Davis also expressed her admiration, honoring Hackman’s lasting impact on cinema. Legendary director Francis Ford Coppola, who had worked closely with Hackman over the years, described him as “magnificent in his work and complexity,” a sentiment echoed by many in Hollywood who had come to know Hackman as both a remarkable actor and a deeply thoughtful individual.
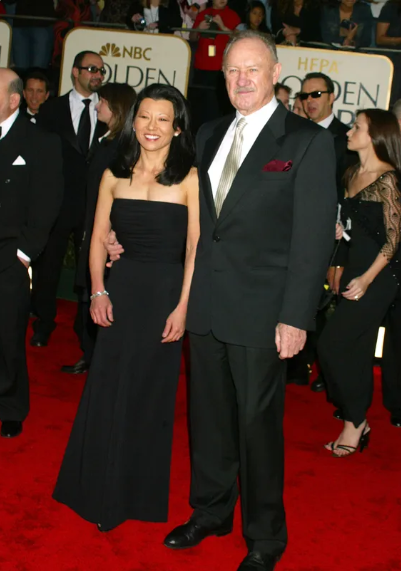

Betsy Arakawa and Gene Hackman at the 60th Annual Golden Globe Awards on January 19, 2003, in Beverly Hills, California. | Source: Getty Images
For Hackman’s children — Christopher, Elizabeth, and Leslie — the loss was profoundly personal. Leslie reflected that, to them, their father was “always just Dad and Grandpa,” emphasizing the quieter, more intimate side of the actor’s life that was far removed from his Hollywood persona.
However, amid the grief and confusion surrounding their deaths, a surprising error regarding the family’s beloved pets added yet another layer to the unfolding tragedy. As investigators dug deeper into the circumstances, it became clear that there were missteps in the handling of the animals, which only intensified the family’s distress during an already overwhelming time.

Gene Hackman and Betsy Arakawa at the Mike Tyson vs. Michael Spinks fight at Trump Plaza on June 27, 1988, in Atlantic City, New Jersey. | Source: Getty Images
How Gene Hackman’s Dog Was Misidentified
Early reports surrounding the scene of the discovery contained a notable error regarding the family’s pets. Authorities initially claimed that the deceased dog found near Betsy was a brown German shepherd. However, Joey Padilla, the owner of Santa Fe Tails pet care facility, quickly clarified the mistake. He confirmed that the dog in question was not a German shepherd, but rather Zinna, a kelpie mix, who had been a beloved companion to the Hackman-Arakawa family.
This misidentification added to the confusion surrounding the case, highlighting the sensitive nature of the investigation and the challenges faced by authorities as they pieced together the details of that fateful day.
Padilla spoke fondly of the deep bond between Betsy and the dog that died, sharing that Zinna “was always attached to Betsy at the hip.” He recalled how the kelpie mix had come into their lives as a returned shelter dog, but under Betsy’s care, Zinna transformed into a devoted and loving companion. “She went from being a returned shelter dog to this incredible companion under Betsy’s hand,” Padilla said, underscoring the special relationship the two shared.
This emotional connection only added to the heartbreak surrounding the tragedy, as it painted a picture of a family deeply intertwined with their pets, and highlighted the personal loss felt not only by the Hackman-Arakawa family but also by those who knew them.

Sheriff’s Office spokesperson Denise Avila acknowledged the misidentification, explaining that deputies are not specifically trained to accurately identify dog breeds during investigations of this nature. She assured the public that while the mistake had been made, steps were taken to ensure the surviving dogs were well cared for. In the aftermath, Bear and Nikita, the two surviving pets, were placed into appropriate care, ensuring their well-being during what was already a difficult time for the family.
The mix-up surrounding Zinna’s identity, while minor in the grand scope of the investigation, underscored the complexity of the situation and added another layer of emotional weight to an already tragic series of events.

As investigators corrected these early missteps, a deeper and more unsettling mystery surrounding Arakawa’s sudden death began to take shape. While Hackman’s cause of death was eventually traced to natural causes related to his age and health conditions, Arakawa’s passing raised more questions. The circumstances surrounding her death seemed out of place, and as the investigation progressed, it became clear that there was much more to uncover than initially thought.
Suspicion grew as authorities dug into her medical history, prescription medications, and possible underlying conditions that may have contributed to her untimely death. Was it a tragic accident, a hidden health issue, or something else entirely? This new line of inquiry would soon unravel further complexities, deepening the mystery that had already shocked the public.
Gene Hackman’s Wife Died of a Rare Virus: What Is Known About It?
As the investigation into Betsy Arakawa’s death progressed, a rare and unsettling cause was uncovered. Arakawa’s death was eventually attributed to a disease transmitted by rodents. Dr. Heather Jarrell, the chief medical examiner at the New Mexico Office of the Medical Investigator, confirmed that Arakawa’s autopsy revealed no signs of trauma, either internal or external. Instead, the microscopic findings pointed to hantavirus pulmonary syndrome (HPS), a deadly illness contracted through exposure to rodent urine, droppings, or saliva.
HPS is a rare but serious disease, most commonly found in rural areas and transmitted by rodents like deer mice. The virus can cause severe respiratory symptoms and is often fatal if not treated quickly. Dr. Jarrell’s report indicated that the microscopic evidence found in Arakawa’s lungs was consistent with the early stages of HPS, which likely led to her sudden and tragic death.
This revelation added a shocking twist to the already mysterious circumstances surrounding the couple’s deaths. While Hackman’s passing was attributed to natural causes, Arakawa’s death from such a rare virus left many searching for answers about the environment she and Hackman had lived in, and whether there was an unnoticed risk that led to her illness.

Gene Hackman and Betsy Arakawa photographed at Elaine’s while promoting his book “Wake of the Perdido Star” on November 3, 1999. | Source: Getty Images
Dr. Heather Jarrell confirmed that laboratory tests were positive for hantavirus, providing the definitive cause of Arakawa’s death. Further testing ruled out other potential causes, including COVID-19, influenza, and carbon monoxide poisoning, all of which came back negative. Additionally, the prescription medications found at the scene, primarily thyroid-related pills, were thoroughly investigated and ruled out as contributing factors to her death.
This conclusion painted a grim and rare picture: Arakawa had succumbed to a virus contracted from rodent exposure, a tragic and unexpected event that left many questions about how the virus could have been transmitted within their home. The negative tests for other potential causes, along with the elimination of the medications, only further confirmed the unusual and rare nature of her passing.
As the investigation into Arakawa’s death came to a close, the focus shifted to understanding how the couple might have been exposed to hantavirus, with the mystery of their deaths now marked by both a profound sadness and an eerie twist of fate.

Dr. Heather Jarrell presents autopsy findings in Bety Arakawa’s death, posted on March 8, 2025. | Source: YouTube/FoxNews
While Dr. Jarrell identified the immediate cause of death, state public health officials played a critical role in explaining the broader threat posed by hantavirus in New Mexico. Dr. Erin Phipps, New Mexico’s state public health veterinarian, offered a detailed briefing to the public, shedding light on the nature of the virus.
“There are many different types of hantaviruses found worldwide. These viruses are zoonotic, meaning they are transmitted from animals to humans,” Dr. Phipps explained. “Hantaviruses are carried by rodents. The hantavirus found in New Mexico — the Sin Nombre virus — is prevalent throughout the state, primarily in deer mice, but also in other rodents.”
The Sin Nombre virus is the most common strain found in New Mexico, and it is transmitted when humans inhale particles of rodent urine, droppings, or saliva. This explanation underscored the potential risk in rural and semi-rural areas where human homes can unknowingly be exposed to infected rodents.
This revelation about the local prevalence of hantavirus added a layer of context to the tragedy, suggesting that exposure could have occurred within the couple’s home or property, though how and when the virus was contracted remained unclear.

Dr. Erin Phipps discusses hantavirus risks after the Hackman investigation, posted on March 8, 2025. | Source: YouTube/FoxNews
Although hantavirus infections are rare, the risks associated with the disease are severe. Dr. Erin Phipps explained that hantavirus pulmonary syndrome (HPS) is a rare but potentially fatal illness caused by hantaviruses. While only a handful of cases are reported each year in New Mexico, the disease’s severity cannot be overstated. “Over the past five years, New Mexico has confirmed between one and seven hantavirus infections in humans each year,” she added.
The rarity of the disease doesn’t diminish the deadly impact it can have. HPS typically presents with flu-like symptoms but rapidly progresses to severe respiratory distress. Given the low incidence of cases, public health officials emphasized that awareness and preventative measures were crucial to limiting exposure, particularly in areas where deer mice and other rodents are prevalent.
Arakawa’s death, though part of the small number of reported cases, highlighted the unpredictable nature of hantavirus and the risks it posed even in seemingly controlled environments. This grim reminder of the virus’s potential impact added to the already tragic circumstances surrounding the couple’s passing.
Since tracking began, New Mexico has recorded a total of 136 hantavirus infections, with five of those cases occurring in Santa Fe County. Dr. Phipps stressed the gravity of the situation, noting, “This is a serious disease — 42% of these infections here in New Mexico were fatal.” The high fatality rate underscored the dangerous nature of hantavirus pulmonary syndrome, making it one of the most severe public health threats in the region, despite the relative rarity of infections.
This statistic served as a stark reminder of how deadly hantavirus can be, particularly when cases are not identified early enough. With such a high fatality rate, the discovery of Arakawa’s infection, along with its connection to rodent exposure, drew significant attention to the broader risks faced by residents of New Mexico, especially in rural and semi-rural areas.
The combination of its rarity, high mortality rate, and potential for human transmission made hantavirus a critical issue for health officials, particularly in areas where the virus is known to circulate.Following Arakawa’s death, the New Mexico Department of Health launched an environmental investigation of the Hackman property to assess potential risks to the family and others. On March 5, a risk assessment team visited the main residence and surrounding structures to determine the level of danger posed by hantavirus to first responders, family members, and anyone who might have been exposed to the environment.
The team carefully inspected the property for signs of rodent activity, such as droppings, nests, and urine, which could indicate the presence of the Sin Nombre virus. In particular, they focused on areas where rodents were likely to have entered the home, including attics, basements, and any cracks or openings in the structure. The investigation was crucial in determining whether the property posed a continued risk and in preventing further exposure to the deadly virus.
The findings of this environmental assessment were significant for public health efforts in the region, especially considering the rarity and severity of hantavirus infections. It also served as a precautionary step to ensure the safety of anyone who might have been on the property during the time of Arakawa’s illness.

Entrance to Santa Fe Summit, where Gene Hackman and his wife, Betsy Arakawa, live, after authorities discover their bodies on February 26, 2025. | Source: Getty Images
Dr. Phipps emphasized that the environmental investigation was “critically important to address concerns about health risks to first responders as well as to inform any prevention measures needed to protect the family and other individuals entering the property in the future.” The findings of the risk assessment team were crucial in determining the level of exposure and in providing guidelines for anyone who might enter the property going forward.
The main house itself was deemed low risk for hantavirus exposure, meaning that there were no immediate concerns for those who would continue to visit or live there. However, investigators discovered signs of rodent activity in nearby buildings, which raised concerns about potential exposure in those areas. As a precaution, Phipps advised anyone entering the property to take proper safety measures. She recommended wearing gloves and an N95 mask while cleaning, as these would provide protection against inhaling any harmful particles. Additionally, she stressed the importance of airing out spaces by opening windows or doors for at least 30 minutes to ensure proper ventilation and reduce the risk of hantavirus exposure.
These steps were part of broader public health recommendations to prevent future cases of hantavirus, particularly in rural areas where rodents carrying the virus are more common. The investigation not only informed immediate safety protocols for the Hackman property but also highlighted the ongoing need for awareness and preparedness in communities where hantavirus remains a concern.
Dr. Phipps also stressed the importance of careful cleaning to prevent hantavirus exposure. After ventilating the area by opening windows or doors, she recommended thoroughly spraying the affected surfaces with a 10% bleach solution or a commercial disinfectant. The disinfectant should be left to sit for five minutes before wiping the area with paper towels, which should then be disposed of in a covered garbage can to minimize the risk of contamination.
In her guidance, she also emphasized the need to practice proper hygiene when handling cleaning materials. “Before removing gloves, wash your gloved hands with soap and water or with a disinfectant, and then after removing gloves, wash your hands again with soap and water,” Phipps advised, stressing the importance of minimizing any contact with potentially infected surfaces.
One crucial warning she issued was to never sweep up or vacuum mouse droppings, as this can stir up particles into the air, which can then be inhaled, putting individuals at greater risk of contracting the virus. This added layer of caution further underlined the serious nature of hantavirus transmission and highlighted the specific precautions that needed to be followed to ensure safety.
These detailed instructions were part of a broader public health effort to prevent hantavirus outbreaks and protect individuals who might unknowingly come into contact with rodent-borne viruses.
Phipps closed her briefing with a message of caution and sympathy, underscoring the broader public health impact of hantavirus in the region. “Since hantavirus is found throughout New Mexico, awareness of these risks and how to reduce them is important for all New Mexicans,” she stated. Her words served as a reminder that while the death of Betsy Arakawa was a tragic and rare occurrence, it highlighted the ongoing need for vigilance and education about the risks posed by rodents carrying the virus.
The message was not just about preventing future infections in the immediate area but also about fostering a statewide awareness of hantavirus and the necessary precautions to protect public health. Phipps’ call for awareness was part of a broader effort to educate communities on how to safely coexist with their environment while minimizing exposure to potentially dangerous zoonotic diseases like hantavirus.
While Arakawa’s death was attributed to the rare but dangerous hantavirus, Hackman’s autopsy would soon reveal that his fate was shaped by very different, long-standing health struggles. Unlike Arakawa, whose sudden and tragic passing was linked to an acute and rare viral infection, Hackman’s death was the culmination of years of age-related health issues. The actor’s advanced age, combined with chronic conditions, ultimately led to his passing, confirming what many had feared: his health had been in steady decline for some time.
The autopsy revealed that Hackman had been suffering from various age-related ailments, including heart disease and respiratory issues, which ultimately contributed to his death. This contrast in the causes of death — Arakawa’s acute infection and Hackman’s slow decline due to chronic conditions — further added to the tragic complexity of their final days, leaving family, friends, and the public to grapple with the emotional weight of two very different kinds of loss.
Hackman’s final autopsy revealed a man whose health had steadily declined over many years, marked by a series of chronic conditions that contributed to his death. He had suffered from congestive heart failure, severe atherosclerosis, and chronic high blood pressure — all of which had necessitated multiple major surgeries throughout his life. These procedures included coronary bypass surgery, stent placements, and an aortic valve replacement, highlighting the long-standing strain on his cardiovascular system.
In 2019, Hackman had a bi-ventricular pacemaker implanted to help manage his heart function and stabilize his condition. The pacemaker, designed to assist with heart rhythm and improve the heart’s pumping efficiency, had been crucial in keeping him alive. However, doctors also found clear evidence of old heart attacks, with scarring visible on his heart tissue, confirming that his heart had been under significant stress for years.
These findings painted a picture of a man who had fought bravely against a range of serious health issues but whose body had eventually succumbed to the wear and tear of decades of medical challenges. Unlike Arakawa’s sudden death from hantavirus, Hackman’s passing was the result of a gradual decline, one that had been managed with medical interventions but ultimately was no match for the toll of his conditions.
The autopsy also revealed another deeply significant detail: Hackman had been battling advanced-stage Alzheimer’s disease. Microscopic examination of his brain showed significant neurodegeneration, confirming that the condition had quietly progressed during his later years. This added a heartbreaking layer to the actor’s health struggles, as Alzheimer’s disease likely contributed to his cognitive decline and made the challenges of managing his other chronic conditions even more difficult.
Toxicology tests also uncovered elevated acetone levels in his blood, which suggested that Hackman may have gone through a period of prolonged fasting or experienced metabolic stress. This finding provided insight into possible stress on his body leading up to his death, though it didn’t point to any direct cause of death.
Additionally, tests for hantavirus and carbon monoxide came back negative, ruling out environmental or infectious causes as contributors to his decline. This final confirmation emphasized that Hackman’s death, while deeply tragic, was the result of a combination of long-term health issues rather than any sudden or external factors.
The autopsy painted a complex picture of a man who had faced a series of health challenges — from heart disease to cognitive decline — and who had lived through years of medical battles before finally succumbing to the toll on his body.
Hackman’s passing marked the culmination of years of silent deterioration, with his health battles—ranging from heart disease to Alzheimer’s—ultimately leading to his death. Unlike his wife Betsy, whose tragic passing was tied to the rare and sudden hantavirus infection, Hackman’s decline was a result of long-standing, chronic health conditions, making their deaths starkly different in nature.
As the causes of their deaths became clearer, the public’s focus naturally turned to the fate of Hackman’s remarkable fortune and the complicated family dynamics that followed. The actor, known for his roles in iconic films like The French Connection and Unforgiven, had amassed a significant wealth during his storied career, and with his death, questions arose about the distribution of his estate, particularly in light of the potential complexities within his family.
Hackman’s children, including Christopher, Elizabeth, and Leslie, were likely to be the primary beneficiaries of his estate, but the handling of his wealth could be complicated by personal relationships, any legal decisions made during his lifetime, and the dynamics between his biological family and his late wife’s side of the family.
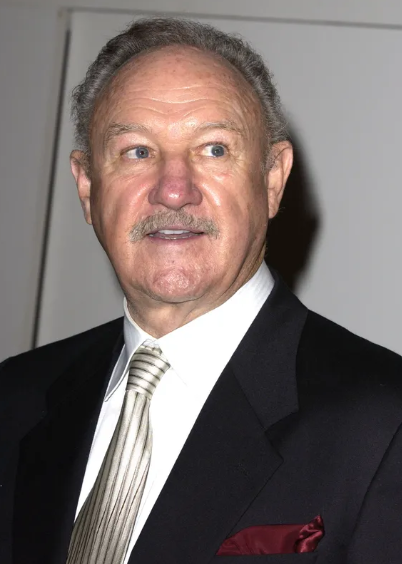

Gene Hackman in the press room at the 60th Annual Golden Globe Awards in 2003, in Beverly Hills, California. | Source: Getty Images

