Understanding Urticaria (Hives): Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment
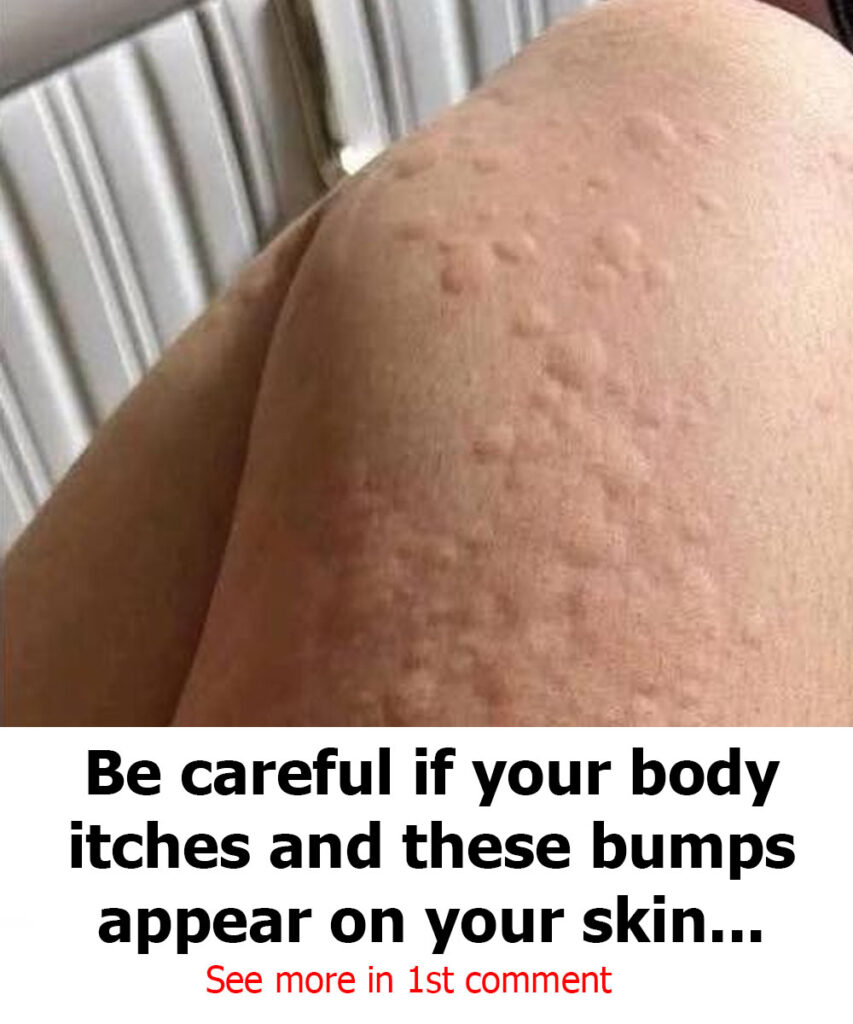
Urticaria, more commonly known as hives, is a skin condition characterized by red, raised, and intensely itchy welts that can suddenly appear anywhere on the body.
These welts vary in size, may join together to form larger patches, and typically fade within 24 hours—although new ones can continue to appear. In some individuals, the condition becomes chronic or recurring, significantly impacting daily life.
What Causes Urticaria?
Hives occur when mast cells in the skin release histamine and other chemicals, leading to fluid leakage from small blood vessels and resulting in swelling and redness.
Common Symptoms:
- Raised, red or skin-toned welts (hives)
- Intense itching (pruritus)
- Welts that come and go quickly but may reappear elsewhere
- Angioedema: Deeper swelling, especially around the lips, eyes, or throat—potentially dangerous if it affects breathing
Types of Urticaria:
- Acute Urticaria: Lasts less than six weeks and is often linked to a specific trigger (e.g., food, medication, infection).
- Chronic Urticaria: Lasts longer than six weeks and may have no clear cause.
- Inducible Urticaria: Brought on by physical factors like pressure, temperature changes, sunlight, or scratching.
Common Triggers:
- Allergens: Foods (e.g., nuts, shellfish), medications, insect stings or bites
- Infections: Viral or bacterial
- Physical stimuli: Cold, heat, pressure, vibration
- Emotional stress: Can worsen symptoms
- Autoimmune responses: Especially common in chronic cases
Treatment and Management:
- Antihistamines: First-line treatment to control itching and reduce welts
- Corticosteroids: Used in more severe or persistent cases
- Trigger avoidance: Identifying and avoiding known causes is key
- Clinical diagnosis: Based on patient history and visible symptoms
With appropriate care and lifestyle adjustments, most cases of urticaria can be effectively managed, even if the condition is chronic or recurring.


